Un site préhistorique exceptionnel contenant des restes d’animaux ayant vécu dans une mer tropicale a été découvert dans le champ d’un fermier du Gloucestershire, en Angleterre.
Les fossiles ont été déterrés sous un champ nourri par une ancienne race de vaches anglaises à longues cornes, et ils ont été étonnamment bien conservés. Bien qu’il date d’environ 183 millions d’années, les fossiles semblent avoir été figés dans le temps.
Les restes de poissons, d’anciens reptiles marins, de calmars, d’insectes rares et plus encore, contenus dans des bétons calcaires préservés en 3D, ont été déterrés pour la première fois par une équipe de paléontologues. Les fossiles proviennent d’une couche interne de roche qui a été découverte pour la dernière fois au Royaume-Uni il y a plus de 100 ans. Il représente une occasion unique de collecter des fossiles d’une époque où cette partie du pays était profondément sous l’eau.
Le site nouvellement découvert se trouve à Court Farm, Kings Stanley, près de Stroud, Gloucestershire. Il a été découvert par Sally et Neville Hollingworth, passionnés de collection de fossiles. Ils ont récemment découvert des restes de mammouths dans le parc aquatique voisin de Cotswold, une découverte qui a été présentée dans un documentaire de BBC One.Cimetière d’Attenborough et de MammothEn 2021.
Sally et Neville ont expliqué : « Ces fossiles proviennent du tout premier[{ » attribute= » »>Jurassic, specifically a time called the Toarcian. The clay layers exposed at this site near Stroud have yielded a significant number of well-preserved marine vertebrate fossils that are comparable to the famous and exquisitely preserved similar fauna of the Strawberry Bank Lagerstätte from Ilminster, Somerset – a prehistoric site of exceptional fossil preservation. Excavations at Kings Stanley over the last week have revealed a rich source of fossil material, particularly from a rare layer of rock that has not been exposed since the late 19th Century.”
Dr. Dean Lomax, a paleontologist and a Visiting Scientist at The University of Manchester, who recently led the excavation of the Rutland ichthyosaur that also dates to the Toarcian geological age, was part of the team and said: “The site is quite remarkable, with numerous beautifully preserved fossils of ancient animals that once lived in a Jurassic sea that covered this part of the UK during the Jurassic. Inland locations with fossils like this are rare in the UK. The fossils we have collected will surely form the basis of research projects for years to come.”
“The site is quite remarkable, with numerous beautifully preserved fossils of ancient animals that once lived in a Jurassic sea that covered this part of the UK during the Jurassic. Inland locations with fossils like this are rare in the UK. The fossils we have collected will surely form the basis of research projects for years to come.”
— Dr. Dean Lomax
Many of the specimens collected will be donated to the local Museum in the Park, Stroud, where they will form a significant part of the museum’s paleontology collections. One of the team members, Alexia Clark, who is the museum’s Documentation and Collections Officer said: “We’re excited to expand our knowledge of the geology of the Stroud District and we are looking forward to a time when we can share these amazing finds with our members and visitors. Being part of the excavation team has been a real privilege and I can’t wait to share details of that experience through our members’ newsletter.”
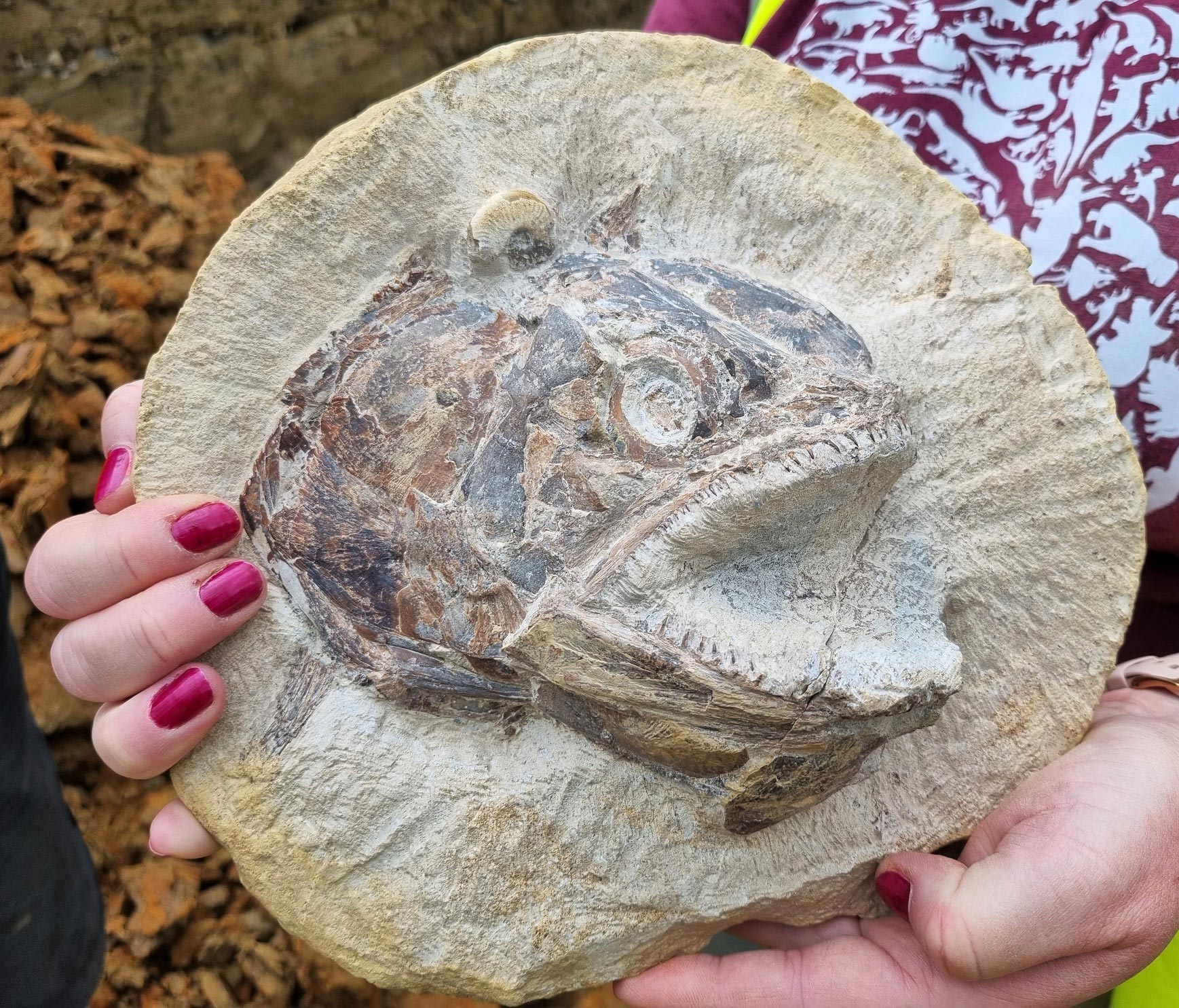
Among the best finds were several fossil fish with excellent details of their scales, fins, and even their eyeballs. One of the most impressive discoveries was a three-dimensionally preserved fish head, belonging to a type of Jurassic fish called Pachycormus. The fish looks as if it is ‘leaping off the rock’ that it was contained inside. A digital 3D model of this fossil has been created by Steven Dey of ThinkSee3D.
Field observations and preparation of the fauna found so far indicate that the Court Farm fossils were rapidly buried, as suggested by the absence of any encrusting animals or burrows in the sediment. The layered concretions around the skeletons formed relatively early before the sediments were compacted, as the original sediment layering is preserved. These concretions prevented further compaction and compression from the overlying sediments during burial and thus preserved the fossils in three-dimensional time capsules.
Neville added, “Using the latest fossil preparation and imaging techniques to understand this unique fauna in more detail will create a rich repository. Also, we will leave a permanent reference section after excavations have concluded. Given the location and enthusiasm from the landowner and local community to be involved it is hoped to plan and develop a local STEM enrichment program as there will be opportunities for community groups and local schools to be involved in the research, particularly from the Stroud area with a focus of targeting audiences in areas of low STEM capital.”
The landowner, Adam Knight, said: “I’m delighted that after the initial work that Sally and Nev did over three years ago we now have a full-scale dig on the farm involving a range of fossil experts from The Natural History Museum, The University of Manchester, University of Reading and The Open University. On Friday we were also joined by Emily Baldry (16) on a day’s work experience before she goes to University to study paleontology – it’s wonderful to see her enthusiasm for her chosen profession. It has been a real pleasure to host the dig and I’m excited to see the results of what has been found.”
The team of paleontologists is very grateful to the Geologists’ Association Curry Fund for financing the excavation phase. Going forward, the team will continue to analyze the specimens and publish their research with the fossils planned for display at Museum in the Park, Stroud, and at the Boho Bakery Café at Court Farm, Kings Stanley, Gloucestershire.







![Les bundles PS5 et Xbox Series X sont disponibles sur GameStop [UPDATE: Sold Out]](https://cdn.vox-cdn.com/thumbor/TRNOGkwP-9WJo6OJdB0e-EeFdk8=/0x146:2040x1214/fit-in/1200x630/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/21990372/vpavic_4261_20201023_0068.jpg)